在上篇spring入门案例,本篇文章讲解如何给对象赋值,即DI操作。本篇总结第一种基于XML的DI。
给对象赋值有两种方式,基于XML的DI和基于注解的DI。
di的实现有两种:
- 在spring的配置文件中,使用标签和属性完成,叫做基于XML的di实现
- 使用spring中的注解,完成属性赋值,叫做基于注解的di实现
di的语法分类:
- set注入(设置注入) : spring调用类的set方法,在set方法可以实现属性的赋值。80%左右都是使用的set注入。(常用)
- 构造注入:spring调用类的有参数构造方法,创建对象。在构造方法中完成赋值。
我们需要重点掌握后者。
基于XML的DI
1、注入分类
set注入(掌握)
A、简单类型
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
System.out.println("setName():"+name);
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
System.out.println("setAge():"+age);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
|
applicationContext.xml配置文件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="myStudent" class="com.thorine.ba01.Student" >
<property name="name" value="zhangsan" />
<property name="age" value="20" />
</bean>
</beans>
|
这样配置之后,应用上篇文章的创建对象方法,创建的Student对象便会带有配置文件中指定的属性。
B、引用类型
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="myStudent" class="com.thorine.ba02.Student" >
<property name="name" value="张三" />
<property name="age" value="22" />
<property name="school" ref="mySchool" />
</bean>
<bean id="mySchool" class="com.thorine.ba02.School">
<property name="name" value="北京大学"/>
<property name="address" value="北京"/>
</bean>
</beans>
|
在Student的类中有一个属性 private School school;School是自定义的一个类,有name 和 address属性。
构造注入(理解)
构造注入是指,在构造调用者实例的同时,完成被调用者的实例化。即,使用构造器设置依赖关系。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
| <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="myStudent" class="com.thorine.ba03.Student" >
<constructor-arg name="name" value="张三" />
<constructor-arg name="age" value="15" />
<constructor-arg name="school" ref="mySchool" />
</bean>
<bean id="myStudent2" class="com.thorine.ba03.Student" >
<constructor-arg index="0" value="李四" />
<constructor-arg index="1" value="25" />
<constructor-arg index="2" ref="mySchool" />
</bean>
<bean id="mySchool" class="com.thorine.ba03.School">
<property name="name" value="北京大学"/>
<property name="address" value="北京"/>
</bean>
</beans>
|
必须在被创建对象的Student类中添加有参构造方法。
1
2
3
4
5
6
| public Student(String name, int age, School school){
System.out.println("============Student类有参数构造方法=============");
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.school = school;
}
|
注意:使用构造注入时,所有的形参都要进行赋值,set注入则可以留空。
2、引用类型的自动注入
对于引用类型属性的注入,也可不在配置文件中显示的注入。可以通过为<bean/>标签设置autowire属性值,为引用类型属性进行隐式自动注入(默认是不自动注入引用类型属性)。根据注入判断标准不同,可以分为以下两种:
- byName:根据名称自动注入
- byType:根据类型自动注入
(1)byName方式自动注入
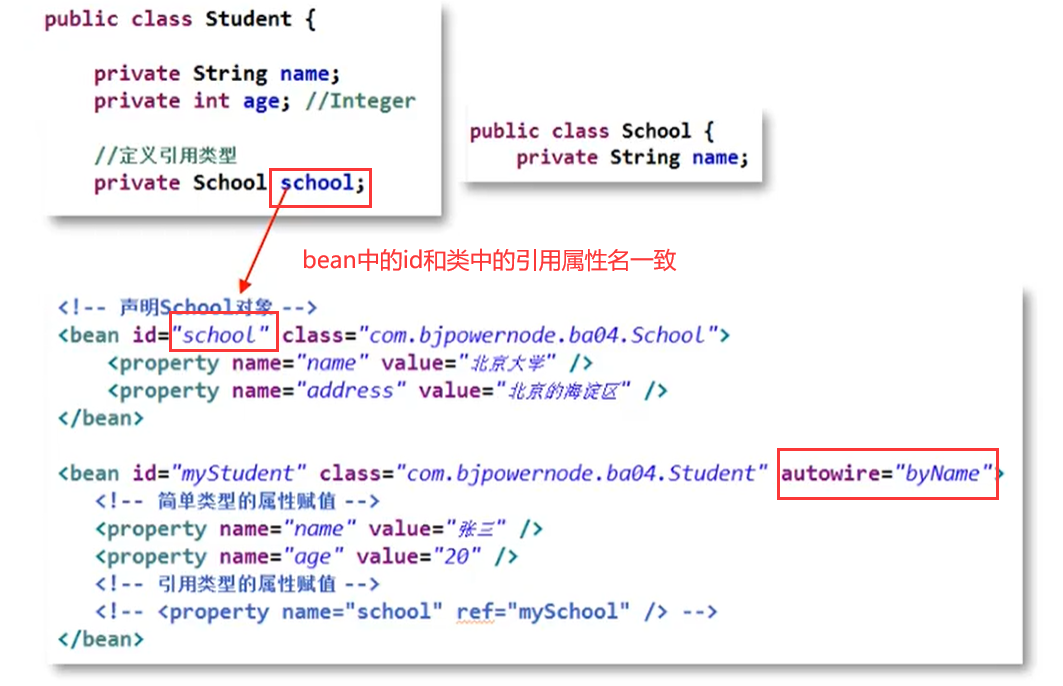
(2)byType方式自动注入
配置文件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
| <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="student" class="com.thorine.ba04.Student" autowire="byType">
<property name="name" value="张三" />
<property name="age" value="22" />
</bean>
<bean id="mySchool" class="com.thorine.ba04.School">
<property name="name" value="北京大学111111111"/>
<property name="address" value="北京"/>
</bean>
</beans>
|
3、为应用指定多个spring配置文件
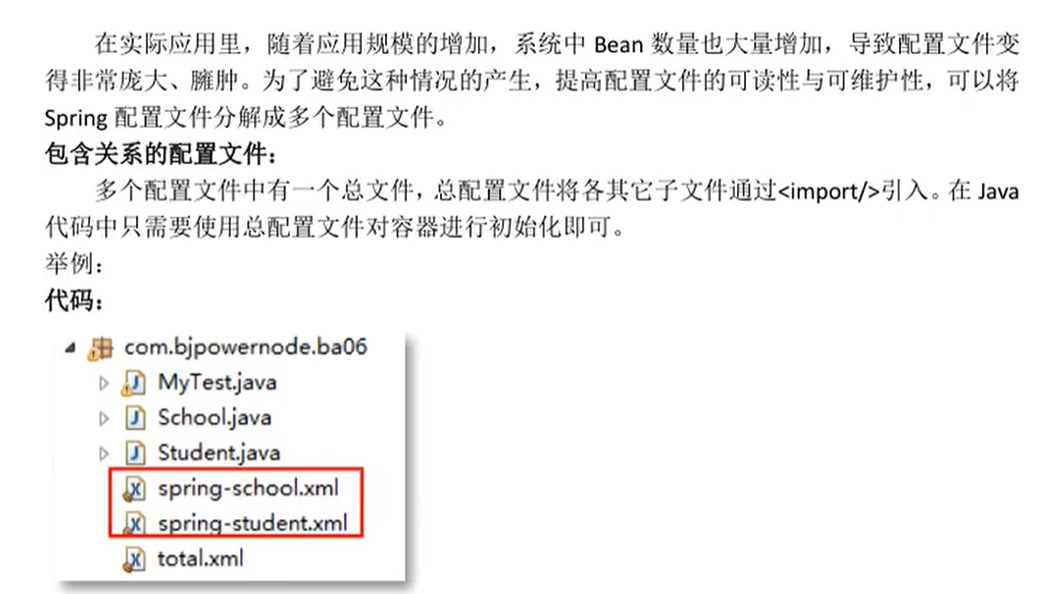
多个配置优势
每个文件的大小比一个文件要小很多。效率高
避免多人竞争带来的冲突。如果你的项目有多个模块(相关的功能在一起),一个模块一个配置文件。
多文件的分配方式:
1.按功能模块,一个模块一个配置文件
2.按类的功能,数据库相关的配置一个文件配置文件,做事务的功能一个配置文件,做service功能的一个配置文件等
例子
三个配置文件.
spring-school.xml
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="school" class="com.thorine.ba05.School">
<property name="name" value="多配置文件"/>
<property name="address" value="北京"/>
</bean>
</beans>
|
spring-student.xml
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="student" class="com.thorine.ba05.Student" autowire="byName">
<property name="name" value="多配置文件"/>
<property name="age" value="88" />
</bean>
</beans>
|
第三个是主配置文件 total.xml
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<import resource="classpath:ba05/spring-school.xml" />
<import resource="classpath:ba05/spring-student.xml" />
<import resource="classpath:ba05/spring-*.xml" />
</beans>
|
其他代码基本一致,注意把调用的config改为 total.xml 即可。


